Cpp & Basic Concepts
CPU side serial code controls(send commands to) CPU side parallel code
- 初始化数据(在CPU内存中)
- 分配GPU内存
- 将数据从CPU内存拷贝到GPU内存
- 启动GPU上的核函数(Kernal)
- 等待GPU计算完成
- 将计算结果从GPU内存拷贝到CPU内存
- 释放GPU和CPU内存
CUDA 函数执行空间限定符
| 限定符 | 执行位置 | 调用位置 |
|---|---|---|
__global__ |
设备(GPU) | 主机(CPU) |
__device__ |
设备 | 设备 |
__host__ |
主机 | 主机 |
kernals are running on the GPU, so we use pointers to access memory
__global__
1 | __global__ void myKernel() |
- must return void
- 如果需要返回结果,必须通过传入指针,让核函数将结果写入GPU内存中
- 使用一种特殊的
<<<...>>>执行配置语法来调用,例如myKernal<<<grid, block>>>(args...);
__device__
1 | __device__ float myDeviceFunction() |
- 这是一个只能在GPU上执行,并且也只能被其他
__global__或__device__函数调用的函数。它通常用于在核函数中实现一些可重用的辅助功能,类似于普通C++代码中的普通函数。 - Inlined by default
for all device code
- No static variables
- lifetime of the program
- on the gpu there is no lifetime concept
- No
malloc()- never
- many of threads tring to allocate, not enough cache to do that
- compiler allows, but performance issue
- GPU内存最好由主机端统一管理。标准的做法是在主机端使用 cudaMalloc() 分配一大块内存,然后将指向这块内存的指针传递给核函数。GPU线程在这个预先分配好的内存区域中进行读写操作。
__host__
1 | __host__ int myHostFunction() |
这就是一个普通的C/C++函数,在CPU上执行,也只能被CPU调用。如果不写任何限定符,函数默认就是 __host__
组合用法
__device__ __host__ void func() VALID
这意味着这个函数被编译了两次:一个版本用于在CPU上调用,另一个版本用于在GPU上调用。这在我们希望CPU和GPU共享某个工具函数(例如一个简单的数学计算)时非常有用。
__global__ __host__ void func() INVALID
这个组合在逻辑上是矛盾的。__global__ 的核心定义是“从CPU调用,在GPU执行”,而 __host__ 的定义是“从CPU调用,在CPU执行”。一个函数不能同时满足这两种执行模式,因此编译器禁止这种组合。
if __global__, it is only __global__ nothing else
pow, sqrt, exp, sin, cos
__powf, __sinf, __logf, __exp
Grid, Block, Thread
这些都是抽象的概念,并非是真是的物理结构,区分这些概念是为了更高效地编程
让不同的线程,拿不同的数据,进行相同的运算
gridDim 与 blockDim 都是dim3
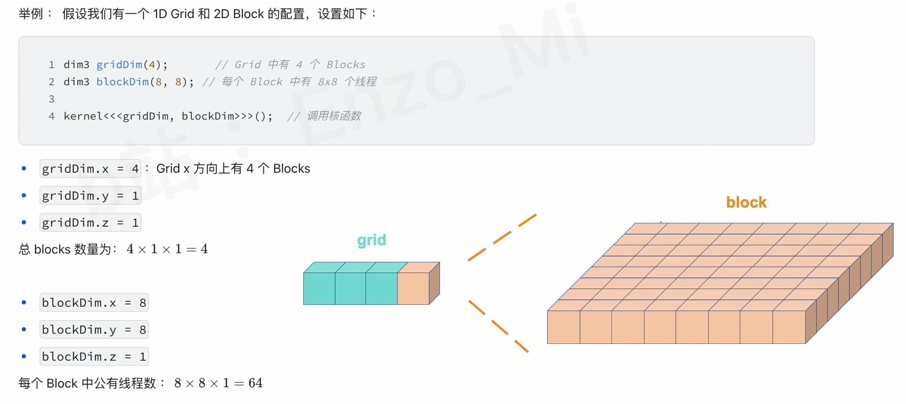
上图中的, 表示1D Grid, 其在x方向上有4个Block,而其他方向上都只有1个Block (默认1个)
1 | dim3 gridDim(4); |
一般的,我们需要设置 block 中的每个维度的线程数为 32 的整数倍
Thread
执行计算的最基本单元。每个线程都会完整地执行一遍核函数 (__global__函数) 的代码。
Treading Model
Real world limitations
- No. of cores Cores/ Transistors for memory
- Power
- Scheduling
Thread Hierarchies
在 __global__ 函数内部,可以直接使用一些内置的只读变量来确定当前线程的位置:dim3 gridDim 网格的维度dim3 blockDim 线程块的维度uint3 blockIdx 当前线程所在Block在Grid中的索引uint3 threadIdx 当前线程在Block中的索引
1D: Thread ID == Thread Index
2D with size (Dx, Dy)
Thread ID of index (x, y) == x + y Dx
3D with size (Dx, Dy, Dz)
Thread ID of index (x, y, z) == x + y Dx + z Dx Dy
1 | // Kernel function to add two matrices |
Block
块内的线程可以相互协作,例如通过共享内存 (Shared Memory) 快速交换数据,也可以进行同步 (__syncthreads())。
一个块内的所有线程必须在同一个流式多处理器 (Streaming Multiprocessor, SM) 上执行
一个 Block 至多可以容纳 1024 个 Thread,这是自开普勒架构(GTX 10系列)显卡之后的规范。
但是,1024个线程并不意味着同一时间会执行1024个,最小的执行单位是Warp
1 | dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16); |
This line declares that each thread block will be a 2D grid containing 16 x 16 = 256 threads. You are creating a small, square team of threads. Here, threadsPerBlock.x is 16 and threadsPerBlock.y is 16. The z-dimension is 1 by default.
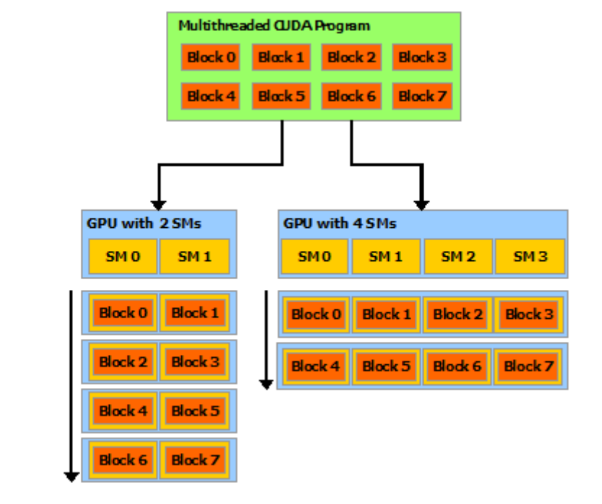
需要注意的是,这里的图片是Scalability的实例,并不是说每次SM就处理一个Block。在同一个Block上运行的threads 确实都在同一个SM上,也就意味着其都可以与L1通信,但是,通过这种办法来达成Block间的通信是不安全的。
不同块之间的线程是无法直接通信和同步的。
Grid
一组线程块的集合。
一个核函数的所有线程都组织在一个网格中
Cpp & Basic Concepts
http://www.tsingloo.com/2025/08/27/d09ff2892db44f09b972a00ed708e798/