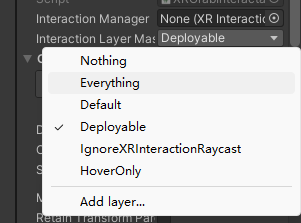
参考资料:
Introduction
QFramework.cs 提供了 MVC、分层、CQRS、事件驱动、数据驱动等工具,除了这些工具,QFramework.cs 还提供了架构使用规范。
QFramework 内置模块如下:
0.Framework:核心架构(包含一套系统设计架构)
1.CoreKit: 核心工具库、插件管理
2.ResKit:资源管理套件(快速开发)
3.UIKit:UI 管理套件(支持自动绑定、代码生成)
4.Audio:音频方案
MVC
MVC模式是软件工程中常见的一种软件架构模式,该模式把软件系统(项目)分为三个基本部分:**模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)**使用此模式有诸多优势,例如:简化后期对项目的修改、扩展等维护操作;使项目的某一部分变得可以重复利用;使项目的结构更加直观。
**视图(View):**负责界面的显示,以及与用户的交互功能。实际在Unity中,这一部分往往指 UI 的呈现。
控制器(Controller):可以理解为一个分发器,用来决定对于视图发来的请求(命令),需要用哪一个模型来处理,以及处理完后需要跳回(通过事件更改)到哪一个视图。即用来连接视图和模型。
**模型(Model):**模型持有所有的数据、状态和程序逻辑。模型接受视图数据(的命令),并返回最终的处理结果(,触发事件)。
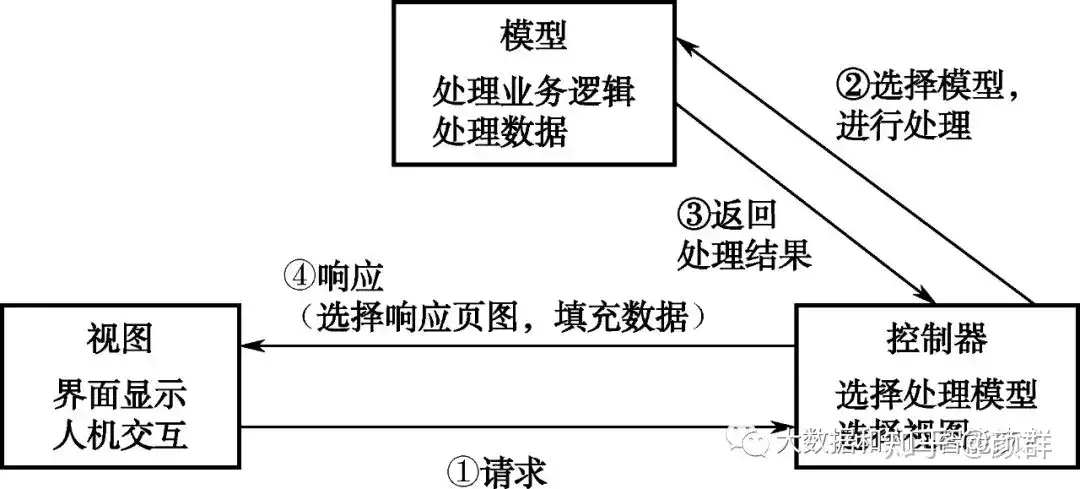
CQRS 命令和查询责任分离
一种将数据存储的读取操作和更新操作分离的模式。
Query 是一个可选的概念,如果游戏中数据的查询逻辑并不是很重的话,直接在 Controller 的表现逻辑里写就可以了,但是查询数据比较重,或者项目规模非常大的话,最好是用 Query 来承担查询的逻辑。

事件驱动
在事件驱动编程中,系统的流程是由外部事件(如用户输入或外部数据更改)驱动的。程序会对发生的事件做出反应。其核心思想是定义并使用事件处理器
用户输入 => 事件响应 => 代码运行 => 刷新页面状态
InputSystem 帮助Unity开发者将用户输入抽象为事件
数据驱动
操作UI(用户输入)=> 触发事件 => 响应处理 => 更新数据 => 更新UI(呈现)
BindableProperty<T> 提供了快速的绑定
Framework
系统设计架构,核心概念包括Architecture、Command、Event、Model、System
Architecture
可以将Architecture视为一个项目模块的管理器(System)的集合, 省去创建大量零散管理器单例的麻烦
使用注册的方式将当前项目所使用的 模块 系统和 工具 添加进内部的IOC容器中,方便管理。
Controller
赋予 MonoBehaviour 脚本对象访问架构的能力
Model
同类的公共数据
架构规范与推荐用法
QFramework 架构提供了四个层级:
- 表现层:IController
- 系统层:ISystem
- 数据层:IModel
- 工具层:IUtility
通用规则
- IController 更改 ISystem、IModel 的状态必须用Command
- ISystem、IModel 状态发生变更后通知 IController 必须用事件或BindableProperty
- IController可以获取ISystem、IModel对象来进行数据查询
- ICommand、IQuery 不能有状态,
- 上层可以直接获取下层,下层不能获取上层对象
- 下层向上层通信用事件
- 上层向下层通信用方法调用(只是做查询,状态变更用 Command),IController 的交互逻辑为特别情况,只能用 Command
表现层
ViewController 层。
IController接口,负责接收输入和状态变化时的表现,一般情况下,MonoBehaviour 均为表现层
- 可以获取 System、Model
- 可以发送 Command、Query
- 可以监听 Event
系统层
System层
ISystem接口,帮助IController承担一部分逻辑,在多个表现层共享的逻辑,比如计时系统、商城系统、成就系统等
可以获取 System、Model
可以监听Event
可以发送Event
数据层
IModel接口,负责数据的定义、数据的增删查改方法的提供
- 可以获取 Utility
- 可以发送 Event
工具层
Utility层
IUtility接口,负责提供基础设施,比如存储方法、序列化方法、网络连接方法、蓝牙方法、SDK、框架继承等。啥都干不了,可以集成第三方库,或者封装API
常用技巧
TypeEventSystem
独立的事件系统,可以理解为群发和广播,创建结构体传递事件内容
1 | public struct PlayerDieEvent { } |
一些简单的事件可以通过 .Register