Introduction
Obi is a collection of particle-based physics plugins for Unity. Everything in Obi is made out of small spheres called particles. Particles can interact with each other, affect and be affected by other objects trough the the use of constraints.
Obi 利用Burst编译器获得高性能的物理计算结果,其完全基于处理器运算,因而可以是全平台支持,(除Obi Fluid以外)各个渲染管线通用。
本文将基于Obi 6.X 讨论如何使用 Obi Softbody 组件
Setup
导入Obi包,不得混杂使用版本不同的Obi assets
可以整个移动/Obi文件夹,或者移除/Obi/Samples文件夹,但是其他的文件不建议修改。
If you’re not using SRPs but the built-in pipeline, it’s safe to delete the /Obi/Resources/ObiMaterials/URP folder. Otherwise Unity will raise an error at build time, stating that it cannot find the URP pipeline installed.
Architecture
Covers Obi’s overall architecture, goes over the role played by all core components (solvers, updaters, and actors) and explains how the simulation works internally.
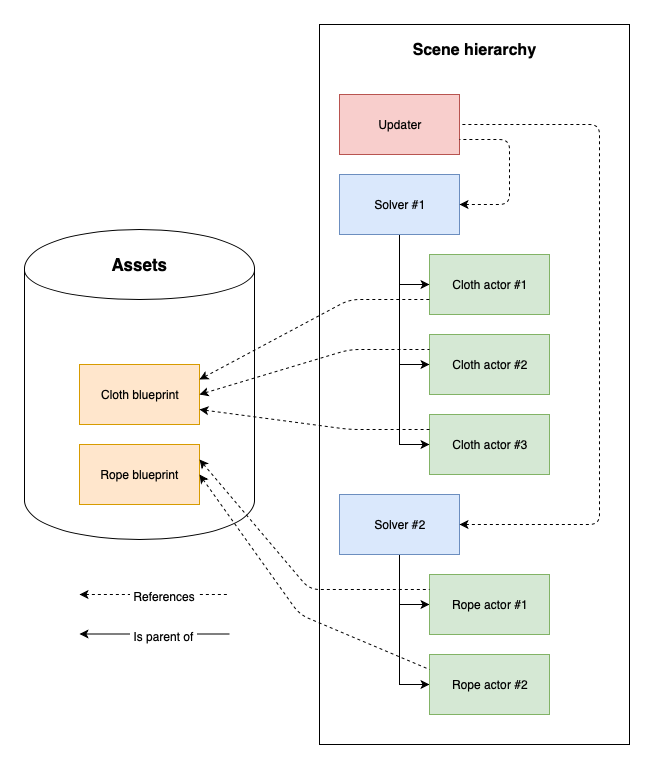
Solvers
Solver 负责进行物理模拟的运算。在 Solver 中提供了一系列可配置的全局物理量与参数,诸如重力(gravity)、惯性尺度(inertia scale)、阻尼(velocity damping)等等。
Each solver will simulate all child actors it finds in its hierarchy, for this it can use multiple backends (Obi 5.5 and up only).
Backends
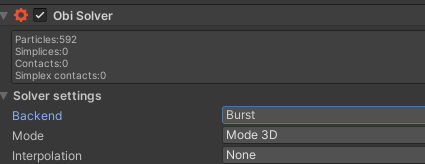
Backend 是 Solver 使用的物理引擎。推荐使用Burst Backend(这也是默认的Backend),其基于job system与Burst编译器,性能比Oni好。
Obi 5.6起,Obi 能够使用 Burst 编译器来处理物理计算。
Using the Burst backend requires having the following Unity packages installed:
- Burst 1.3.3 or newer
- Collections 0.8.0-preview 5 or newer
- Mathematics 1.0.1 or newer
- Jobs 0.2.9-preview.15 or newer
以上的包大多数可以在Package Manager中的Unity Registry中找到,但是一些preview的包,若搜索不到,需要手动添加(you may need to manually locate the packages by URL)
如果导入Burst包后,开启项目时其报一些错误,可以看一下项目路径里是否有中文。
Unity 2022.2之后,Job system packages(对应 Jobs 0.2.9-preview.15 or newer)已经安装,不用额外导入。以上包导入正常后,可以看到,Backend 选择 Burst不会有黄色感叹号。
Performance
官方文档中给出了一些需要着重注意的,与性能相关的选项,详见Performance:
对于不同的Unity版本,窗口可能会有一些变化。
Please note that for normal performance when using the Burst backend in-editor, you must enable Burst compilation and disable the jobs debugger, safety checks and leak detection.
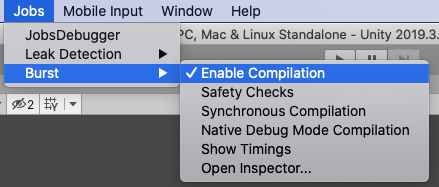
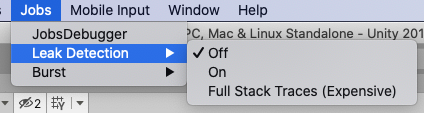
Also, keep in mind that Burst uses asynchronous compilation in the editor by default. This means that the first few frames of simulation will be noticeably slower, as Burst is still compiling jobs while the scene runs. You can enable synchronous compilation in the Jobs->Burst menu, this will force Burst to compile all jobs before entering play mode.
Updaters
ObiUpdater 是一个在特定时间点上推动一个或者多个Solver模拟运算的组件。
A ObiUpdater is a component that advances the simulation of one or more solvers at a certain point during execution.
一般来说,我们会想让Solver的模拟和其他在FixedUpdate()中的物理模拟保持同步。有时也可能为了一些效果希望放在skeletal animation之后,即LateUpdate()中。甚至。我们会希望自己决定何时Update来自Solver的模拟。
一般来说,一个场景中应当使用仅仅使用一个Updater。若如此做,所有在此Updater中的Solver可以合理地拆分任务,从而并行执行模拟。Obi允许一个场景中使用多个Updater,但是需要注意的是, 一个solver必须只能被一个updater引用,否则将导致此solver一帧内被update多次,导致不稳定的结果。
一个没有被任何Updater管理的solver,将不会update它的模拟。
Obi Fixed Updater
此组件将在FixedUpdate()中update模拟。 其会产生最为符合物理的效果,应当在绝大多数时候使用。
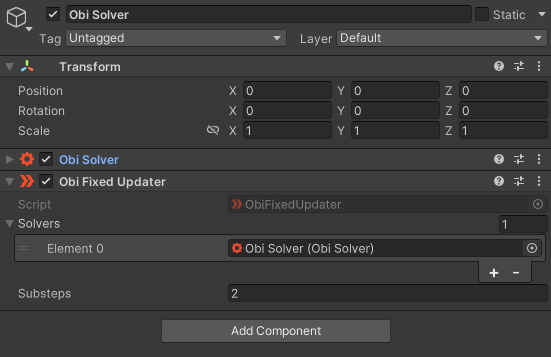
在示例场景中,Obi Solver 与 Obi Fixed Updater 挂载在作为父节点的空物体上。Obi Fixed Updater 存了一份此Obi Solver的引用。
Substeps
Updater 可以将每个物理阶段(physics step)分成更多个子阶段(smaller substeps)。例如,如果Unity的 fixed timestep = 0.02 Substeps = 4,那么每个子阶段将会推进0.02/4 = 0.005 秒的模拟。子阶段越多,结果也就越精确,当然性能也会随之下降。
Collision detection will still be performed only once per step, and amortized during all substeps.
Tweak substeps to control overall simulation precision. Tweak constraint iterations if you want to prioritize certain constraints. For more info, read about Obi’s approach to simulation.
Obi Late Fixed Updater
The late fixed updater will update the simulation after WaitForFixedUpdate(), once FixedUpdate() has been called for all components, and all Animators set to Update Physics have been updated. Use it to update the simulation after animators set to Update Physics have advanced the animation.
在制作布料等等,由角色动画驱动的物理效果时,一般考虑Late Fixed Updater
Obi Late Updater
This updater will advance the simulation during LateUpdate(). This is highly unphysical, as it introduces a variable timestep. Use it only when you cannot update the simulation at a fixed frequency. Sometimes useful for low-quality character clothing, or secondary visual effects that do not require much physical accuracy.
Delta smoothing
This updater will try to minimize the artifacts caused by using a variable timestep by applying a low-pass filter to the delta time. This value controls how aggressive this filtering is. High values will agressively filter the timestep, minimizing the change in delta time over sucessive frames. A value of zero will use the actual time delta for this frame.
ObiActorBlueprint
A blueprint is an asset that stores a bunch of particles and constraints. It does not perform any simulation or rendering by itself. It’s just a data container, not unlike a texture or an audio file. Blueprints are generated from meshes (ObiCloth and ObiSoftbody), curves (ObiRope) or material definitions (ObiFluid).
Actors
布料、绳索、fluid emitter 或者 softbody 的一部分, 都被称为 actors
Actor 接受blueprint(particles and constraints)作为输入。相同的blue print 可以被多个update使用。
Actor 必须作为 solver 的子物体上的组件,这样它才能被模拟包括。在runtime我们可以将一个actor重新放置到一个新的solver下。 At runtime you can reparent an actor to a new solver, or take it out of its current solver’s hierarchy if you want to.

一般需要以下步骤来使用Actor
- Create a blueprint asset of the appropiate type. Generate it, then edit it if needed.
- Create the actor, and feed it the blueprint.
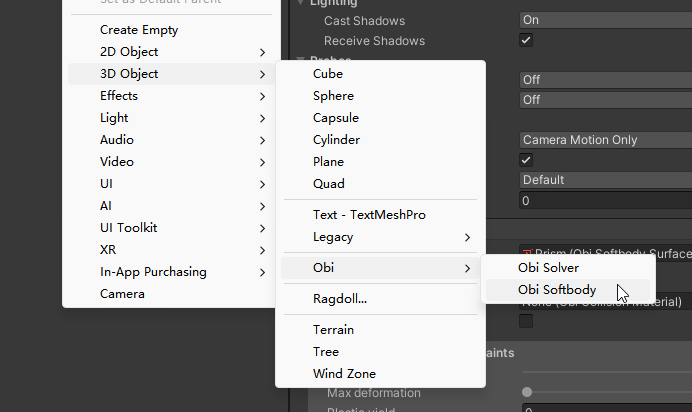
当第一次在场景中创建actor时,Obi将会寻找一个ObiSolver的组件来添加此actor。如果找不到一个合适的solver,它会自己创建一个ObiFixedUpdater
每当Actor被添加到一个Solver时:
Actor会向Solver请求其蓝图所需的粒子。Solver将会给粒子分配index,一个actor所拥有的粒子的index可能不是连续的。
The actor makes a copy of all constraints found in the blueprint, and updates their particle references so that they point to the correct solver array positions.
The number of active particles in the solver is updated.
Simulation
官方文档:Simulation
Obi将所有的物理模拟建模为一系列粒子和约束。Particles are freely-moving lumps of matter, and constraints are rules that control their behavior.
每个约束将选取一些点,以及一些“外部”世界中的信息,包括:colliders, rigidbodies, wind。然后约束会改变粒子的位置,使其满足一些给定的条件。
Obi uses a simulation paradigm known as position-based dynamics, or PBD(参考【物理模拟】PBD算法详解) for short. In PBD, forces and velocities have a somewhat secondary role in simulation, and positions are used instead. 每一步后,PBS会根据约束来改变此时的位置,进而也就改变了速度矢量。
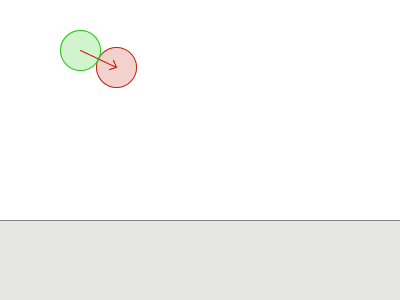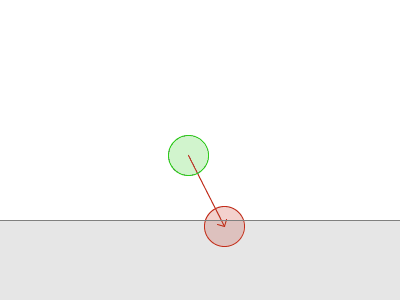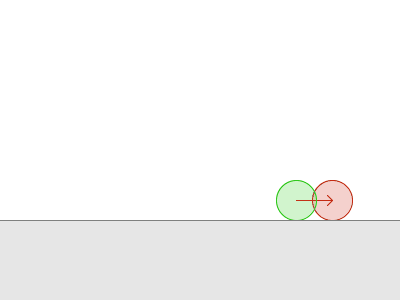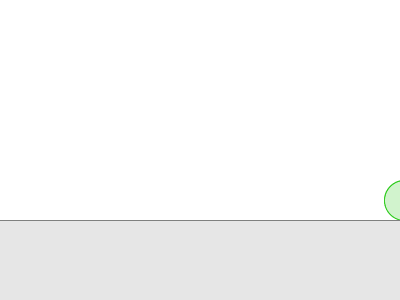
但是一些时候,往往难以找到一个位置满足所有的约束。
Sometimes, enforcing a constraint can violate another, and this makes it difficult to find a new position that satisfies all constraints. Obi will try to find a global solution to all constraints in an iterative fashion. With each iteration, we will get a better solution, closer to satisfying all constraints simultaneously.
Obi 有两种遍历约束的方法:sequential or parallel 。
在Sequential模式中, 每个约束都会被考虑在内,并且与每个约束计算所得出的调整,会立刻被应用,然后再接着处理下一个约束。因此,处理约束的顺序会影响最终的结果。
在Parallel模式中,所有的约束都在第一时间根据当前位置计算,在这之后求取各个调整结果的平均值加以应用。因此,怕parallel不用考虑顺序,然而这会减慢解算的时间。
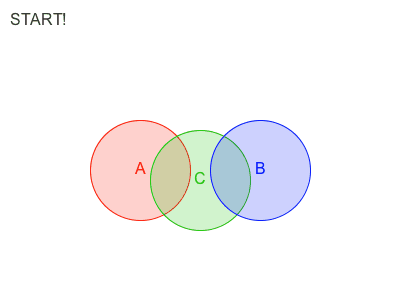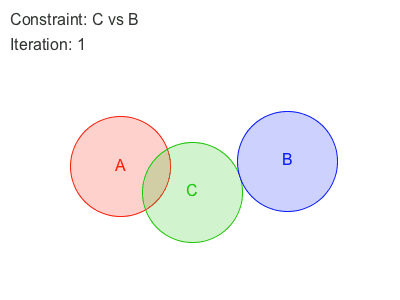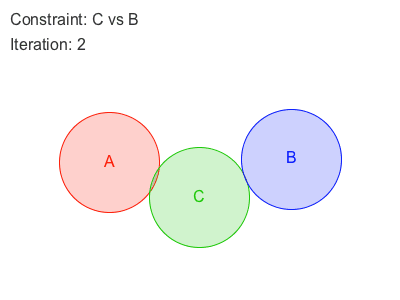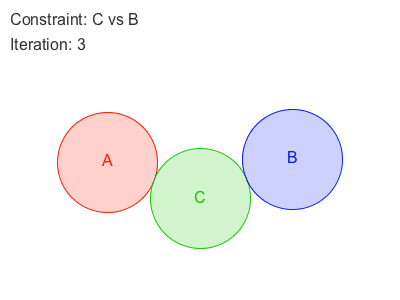
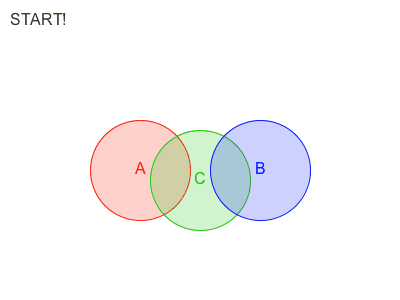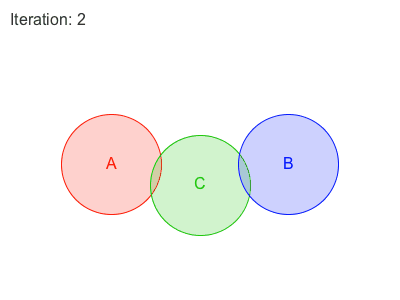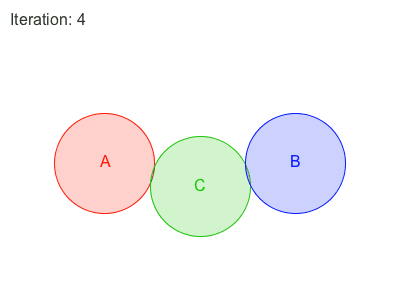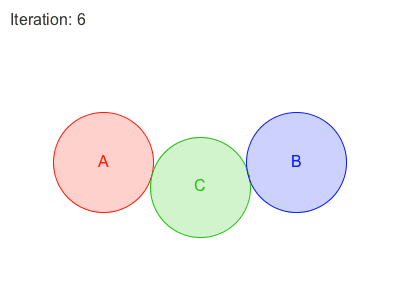
Each additional iteration will get your simulation closer to the ground-truth, but will also slightly erode performance. So the amount of iterations acts as a slider between performance -few iterations- and quality -many iterations-.
An insufficiently high iteration count will almost always manifest as some sort of unwanted softness/stretchiness, depending on which constraints could not be fully satisfied:
- Stretchy cloth/ropes if distance constraints could not be met.
- Bouncy, compressible fluid if density constraints could not be met.
- Weak, soft collisions if collision constraints could not be met, and so on.
对于一些现实中、物理上容易变形的物体,可以索性将其迭代次数调小。
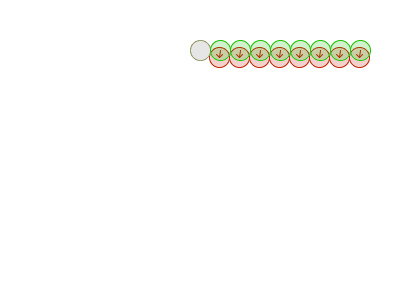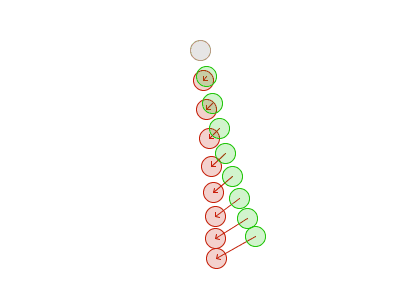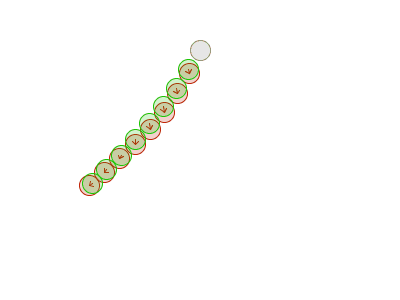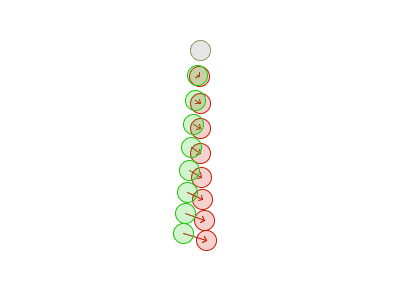
减小timestep size 可以减小(达到物理真实的)迭代循环的次数,当然也会增加消耗,但是增加的消耗比使用多个迭代要少,是划得来的
This can be accomplished either by increasing the amount of substeps in our fixed updater, or decreasing Unity’s fixed timestep (found in ProjectSettings->Time)
Note that reducing the timestep/increasing the amount of substeps also has an associated cost. But for the same cost in performance, the quality improvement you get by reducing the timestep size is greater than you’d get by keeping the same timestep size and using more iterations.
Unlike other engines, Obi allows you to set the amount of iterations spent in each type of constraint individually. Each one will affect the simulation in a different way, depending on what the specific type of constraint does, so you can really fine tune your simulation:
Constraint types
Obi 允许我们为每种约束类型设置其迭代次数。
官方文档详细地给出了各种约束的特性和使用场景:Constraint Types
如果物体is too stretchy or bouncy,可以尝试:
- Increasing the amount of substeps in the updater.
- Increasing the amount of constraint iterations.
- Decreasing Unity’s fixed timestep.
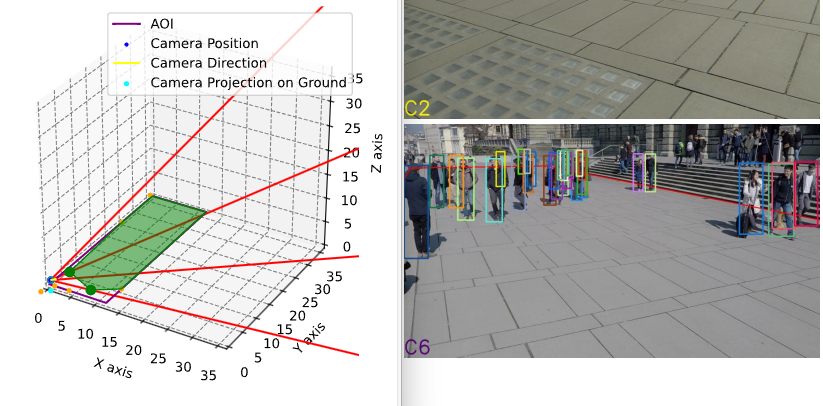
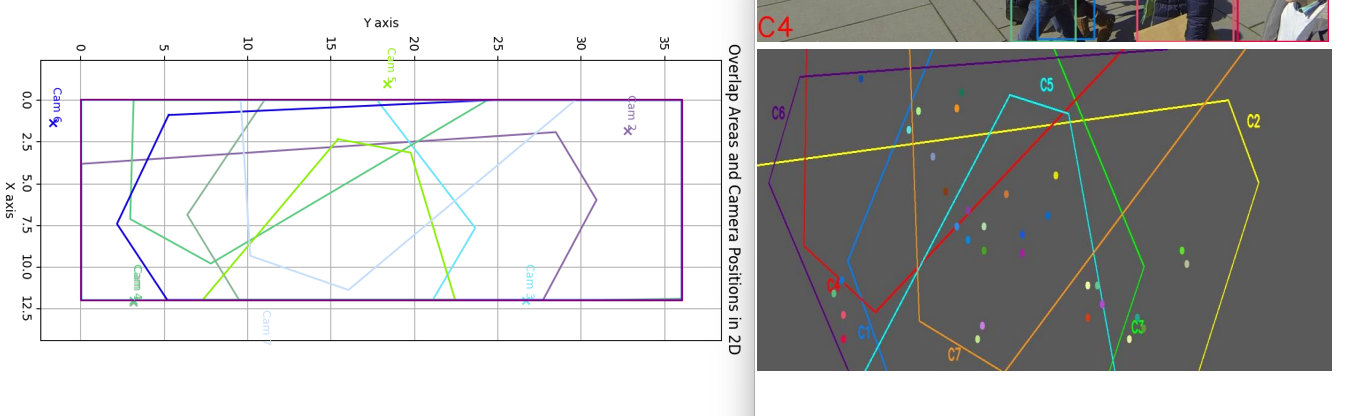
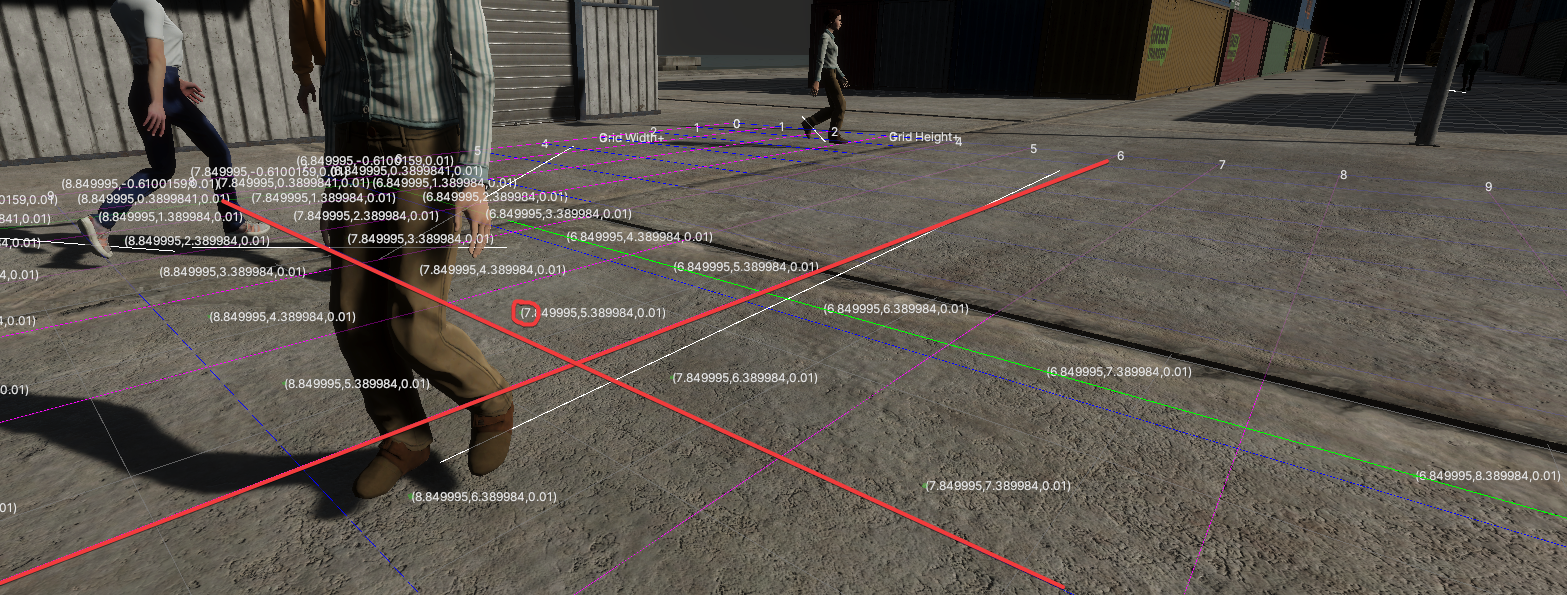
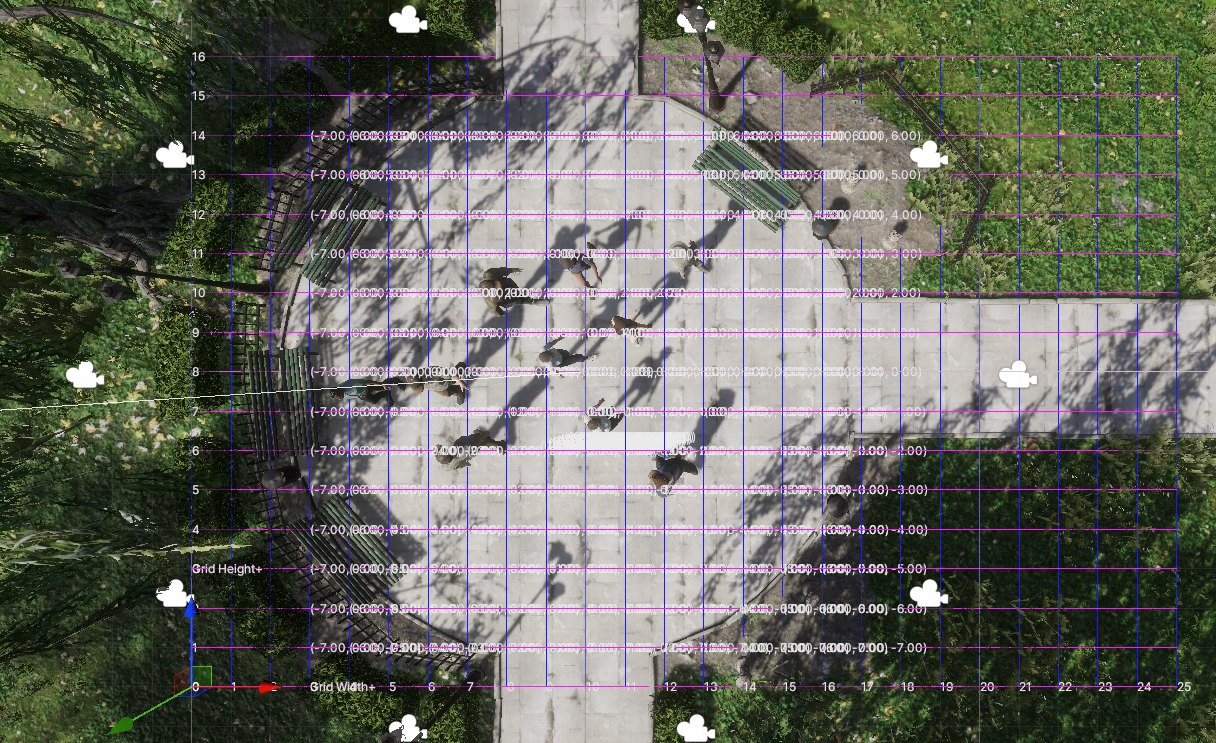

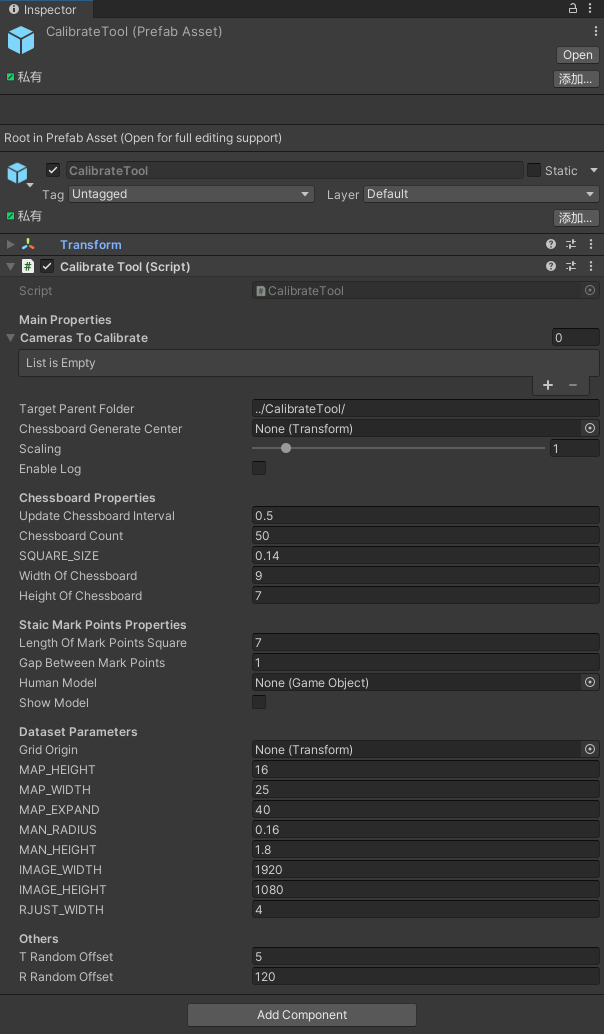
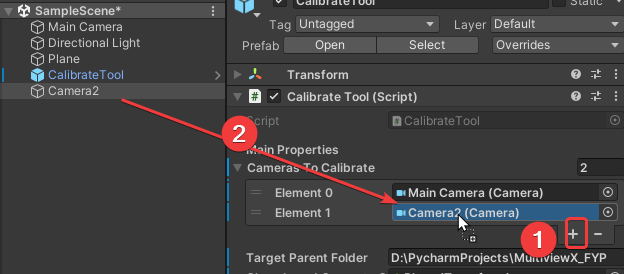
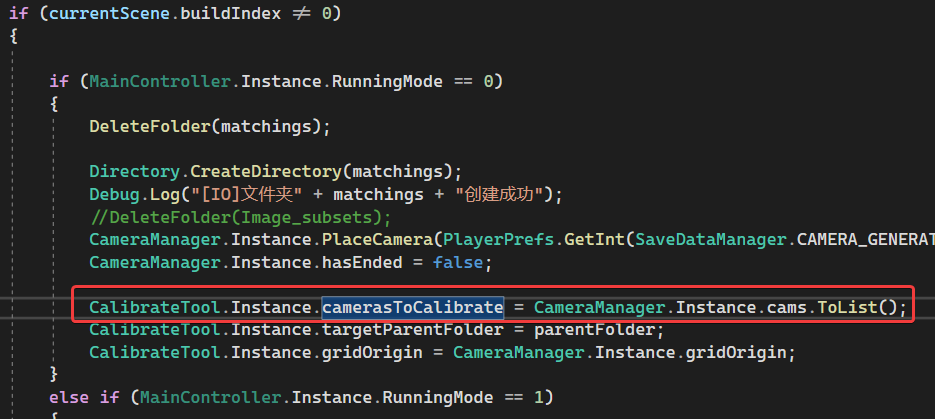

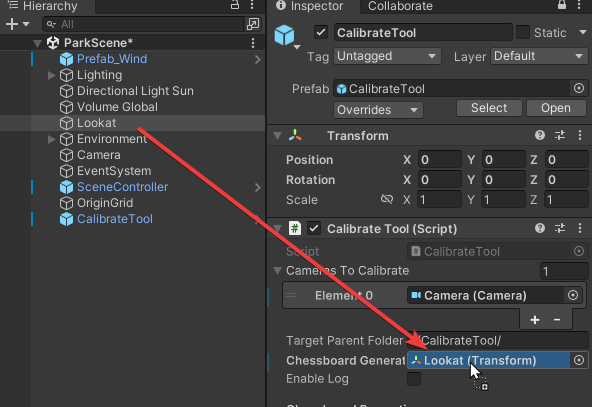
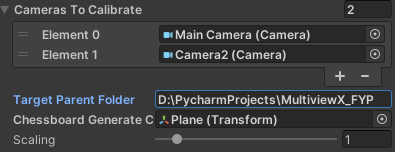
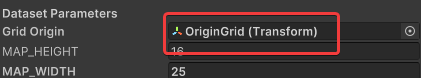
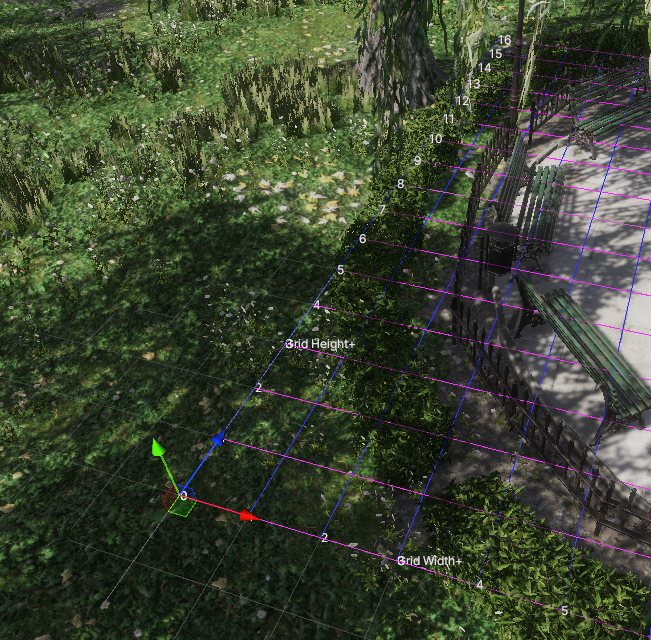
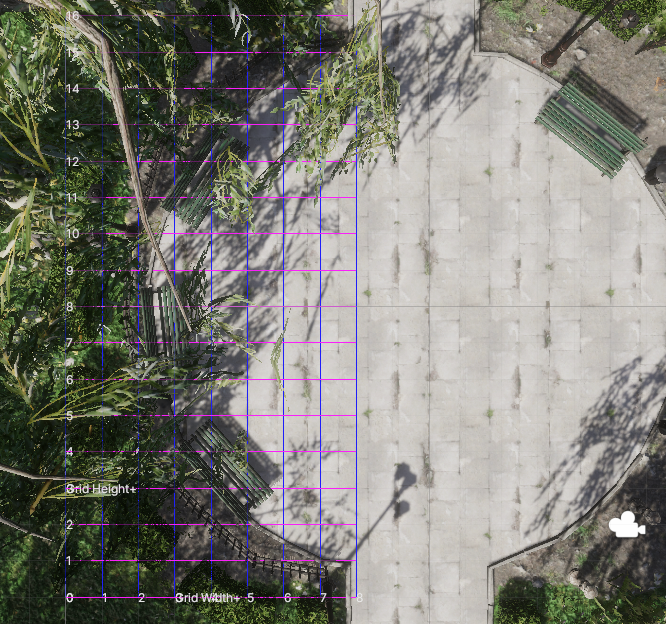


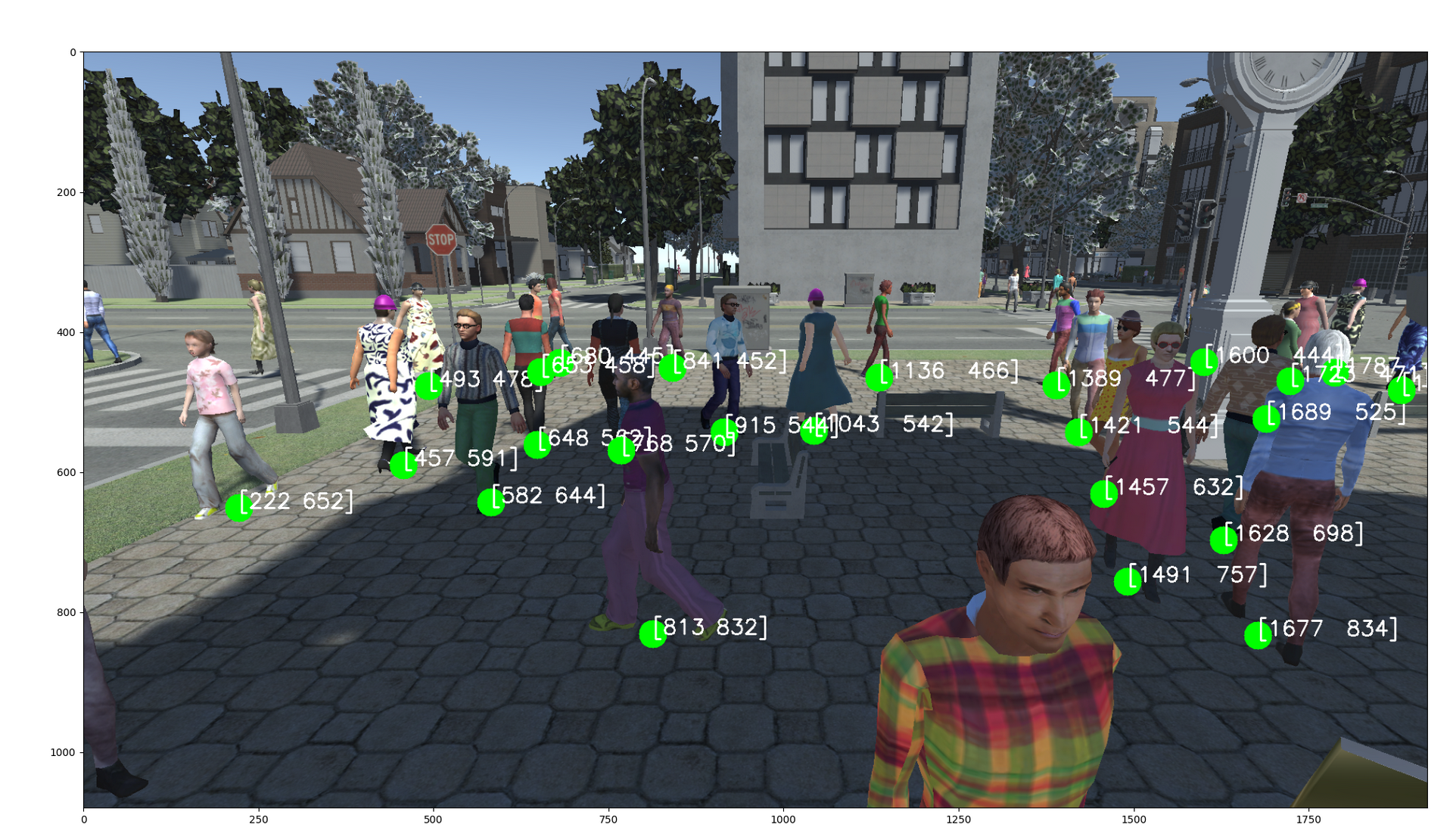
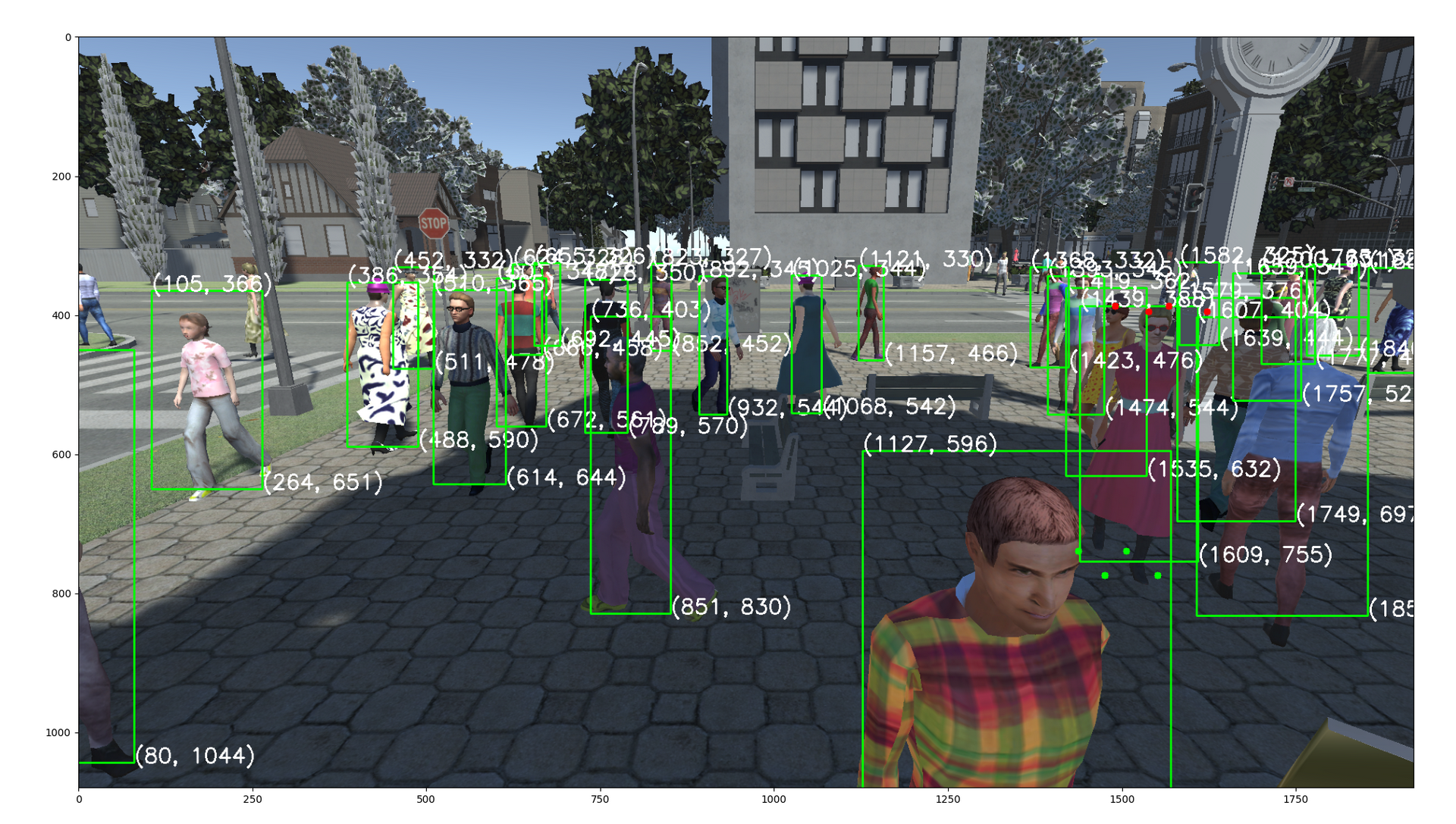
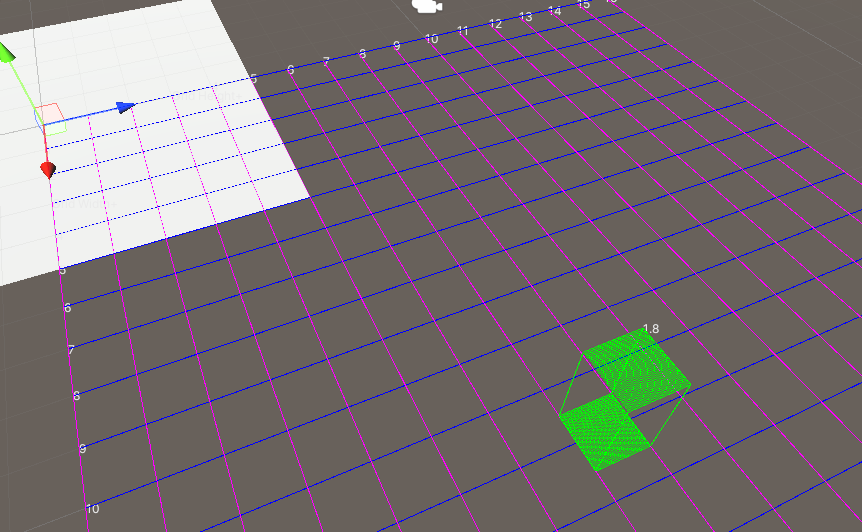
 这就导致用户难以一站式完成CalibrateTool的使用,需要自己手动再去调整人物模型或者场景素材,而往往这种调整还牵扯到matchings(MultiviewX接受的一种输入)的坐标变换,每个人实现matchings的方法都不一样,这里提个醒,坐标变换的顺序必须是: 缩放->旋转->平移。
这就导致用户难以一站式完成CalibrateTool的使用,需要自己手动再去调整人物模型或者场景素材,而往往这种调整还牵扯到matchings(MultiviewX接受的一种输入)的坐标变换,每个人实现matchings的方法都不一样,这里提个醒,坐标变换的顺序必须是: 缩放->旋转->平移。
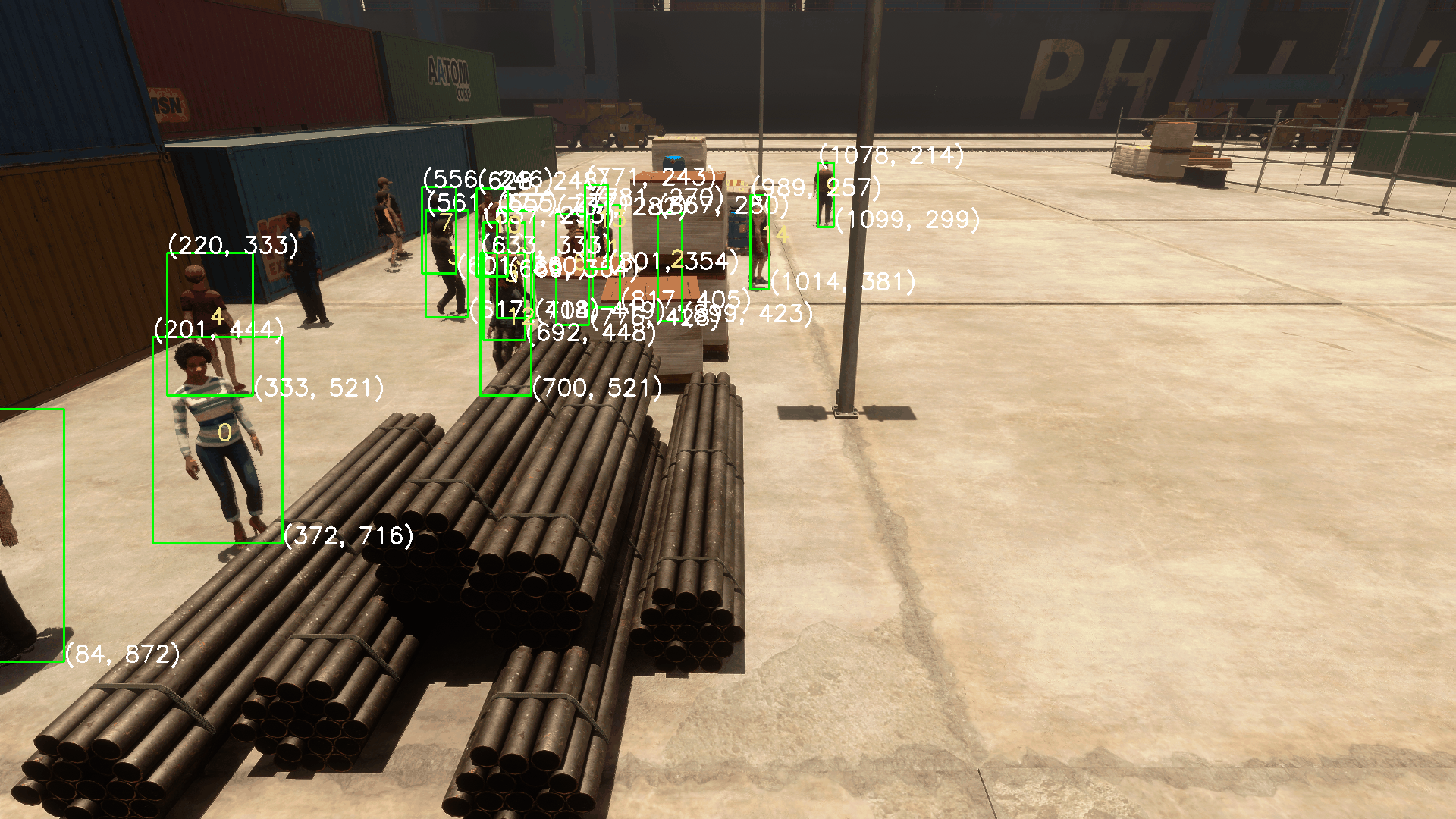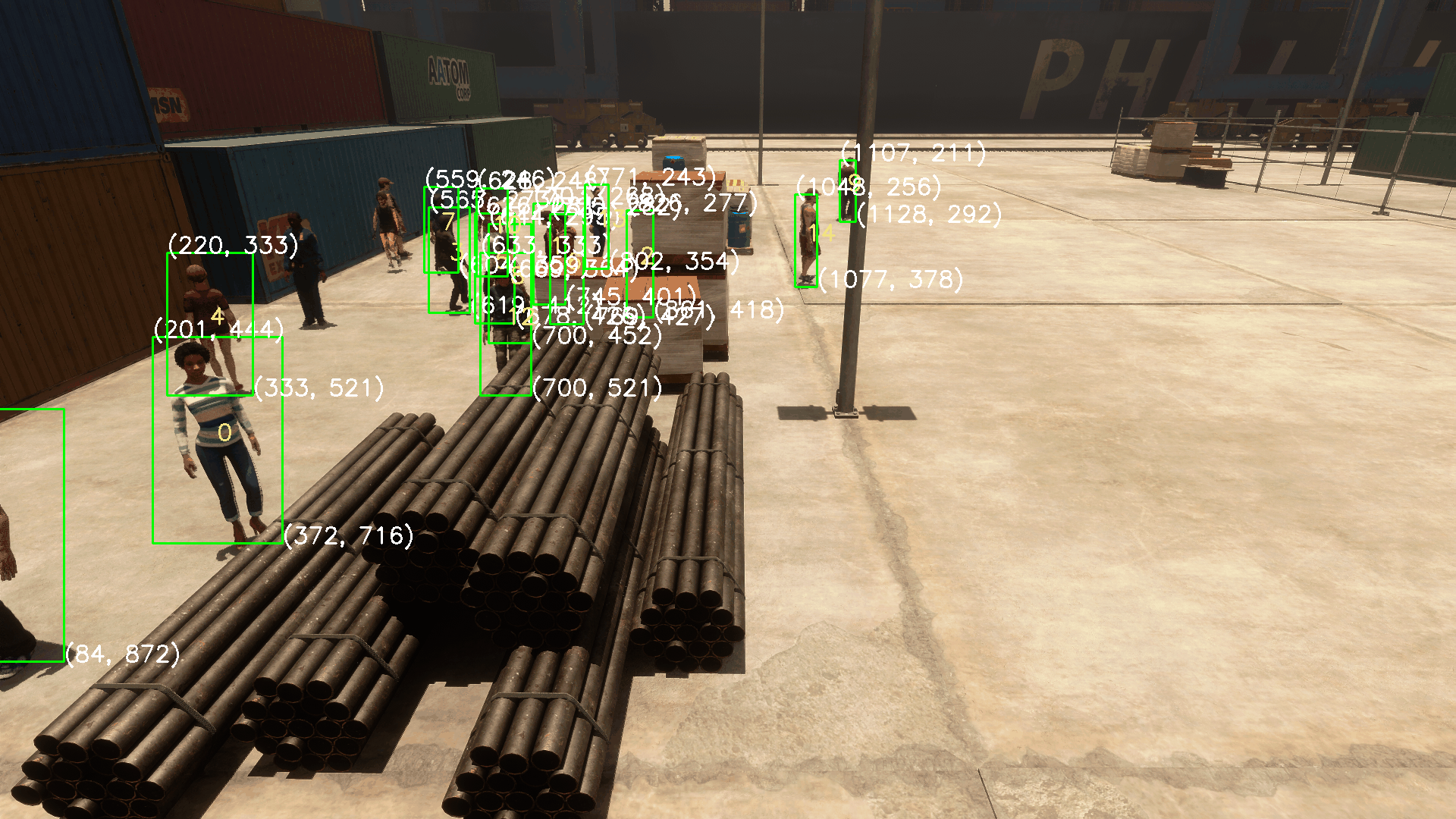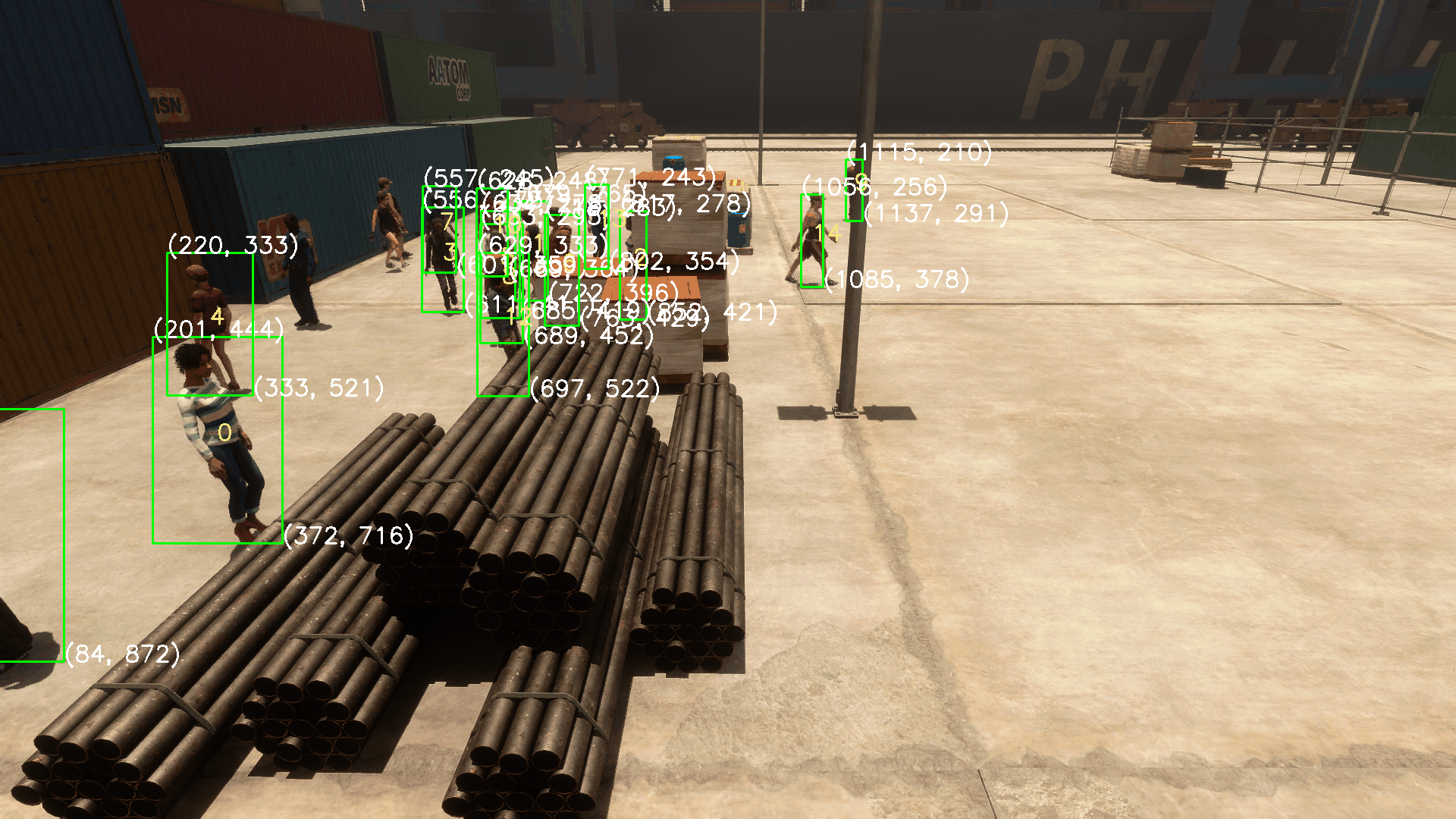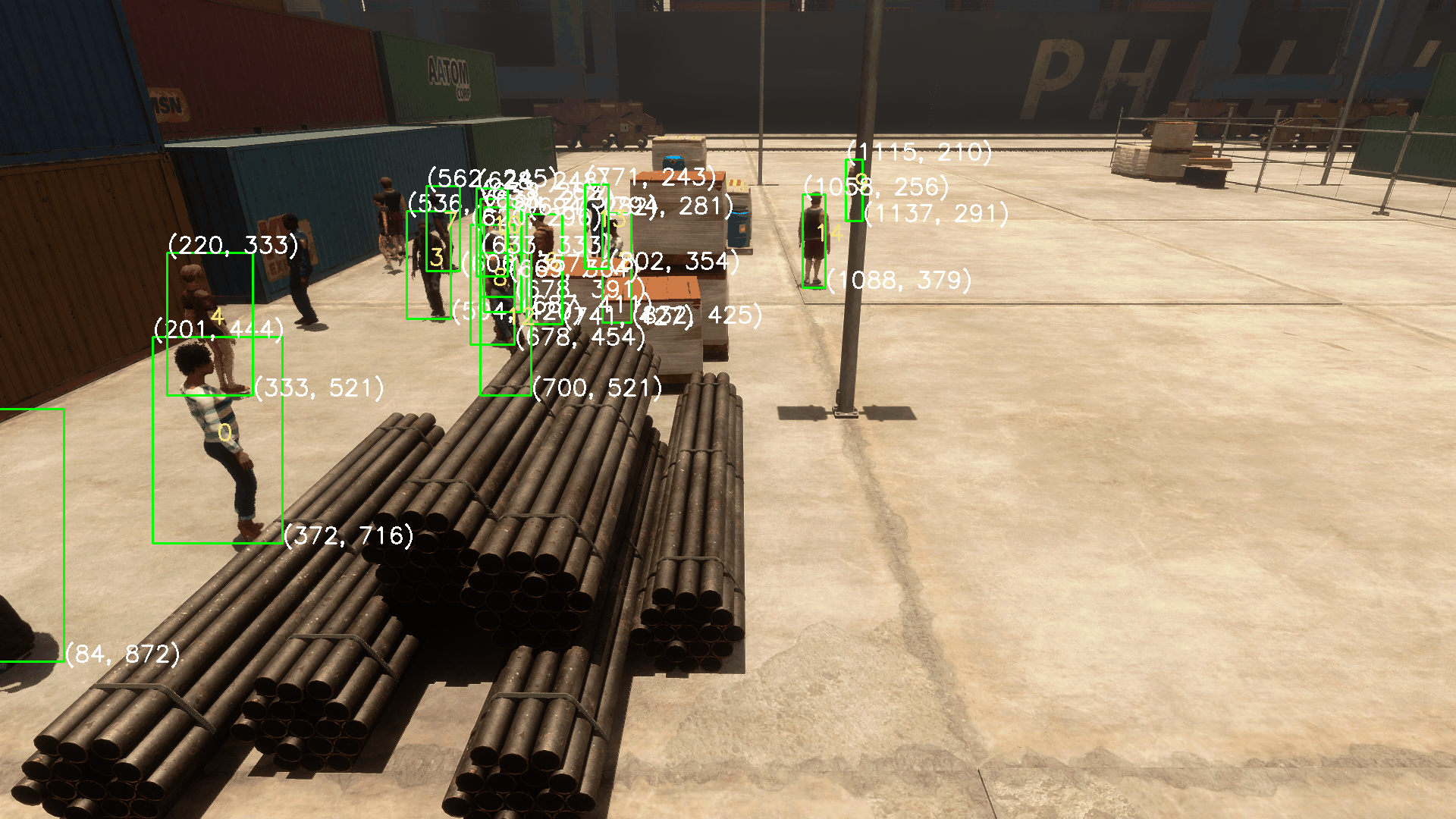
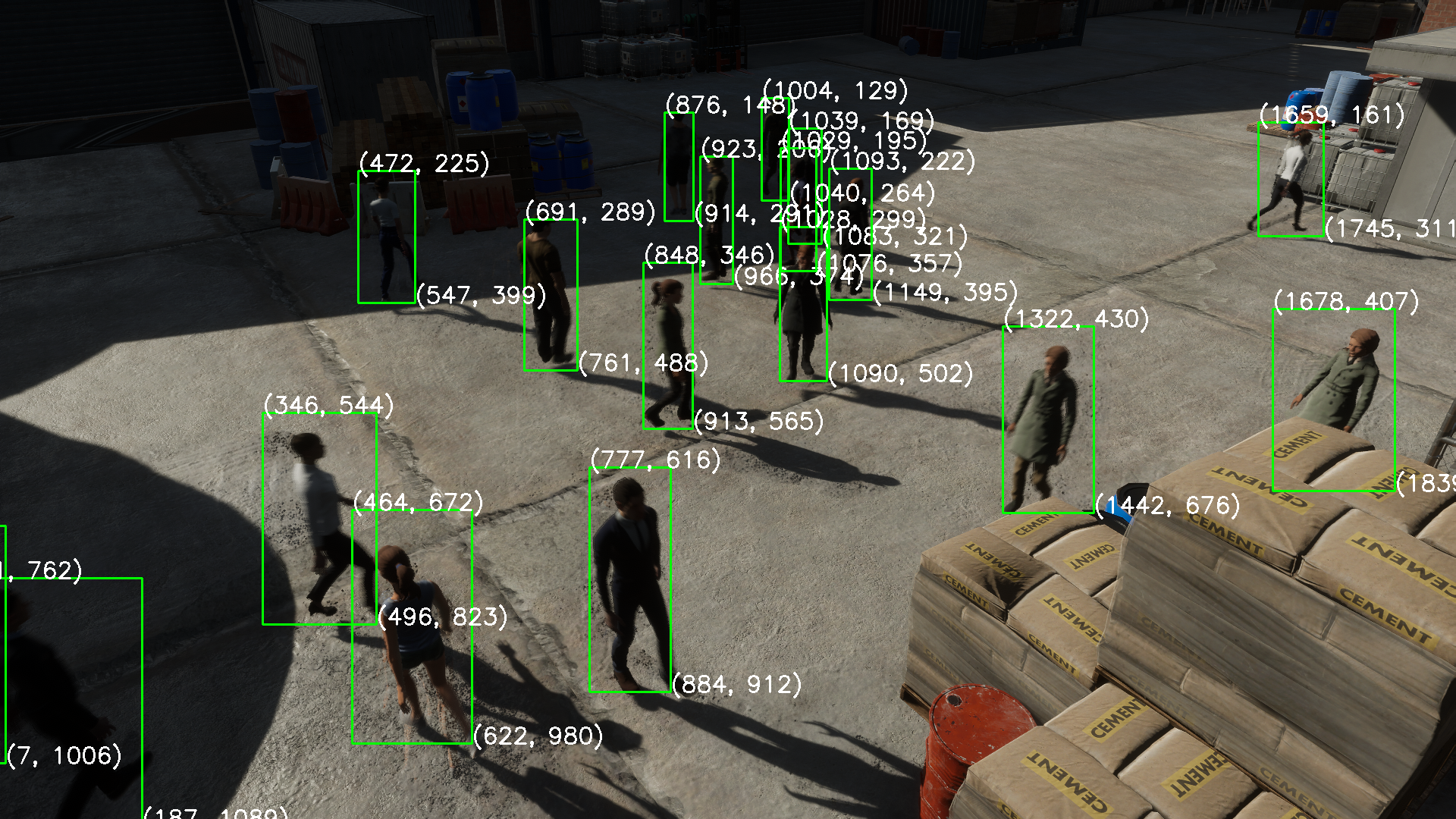
 我们可以注意到,Camera Labelers中有
我们可以注意到,Camera Labelers中有